Space Propulsion Market Report Scope & Overview:
To get more information on Space Propulsion Market - Request Free Sample Report
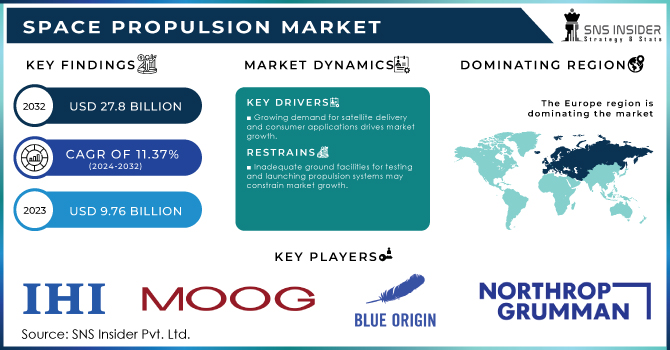
The Space Propulsion Market was recorded at USD 9.76 billion in 2023 and is expected to surpass USD 27.8 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11.37% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
Aerospace systems are used to produce spacecraft, vehicle launchers, tablets/goods, and rovers/spacecraft landers for orbit, station maintenance, air-launch vehicles, and mood control, among others. These systems include chemical generation technologies such as solid, liquid, mixed, and cold technology as well as non-chemical advancing technologies such as electricity, solar, nuclear, and laser propulsion. Thrusters, propellant feed systems, rocket motors, nozzles, reactors, propulsion thermal control, and power processing units are all components utilised in-space propulsion systems (PPU).
The space propulsion market combines chemical and non-chemical use in government and end-of-life military and commercial users. For the end-user, the market is divided commercially between government and defense. The developed economies of North America and Europe are currently at the forefront of the market, considering the strong presence of OEMs in these regions, and emerging economies, especially those from the Asia Pacific region, are expected to be major future markets for space systems. In general, access to space has become more expensive. But prices continue to decline with each passing year as new technologies are developed and the sector sells more. SpaceX, for example, has demonstrated the power of reusable rockets. Other future improvements may include simplification, use of breathable modules, new fuel types, aerospace, and/or more efficient engines. The rapid increase in research and development activities in space propulsion systems by independent actors is expected to stimulate the growth of the space propulsion market during the forecast of Safran, Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc., SpaceX, IHI Corporation, and Northrop Grumman Corporation are some of the leading players working in the space propulsion market. An overview of these companies, their financial analysis, products, and services, and the significant improvements made by them are included in this report.
KEY DRIVERS
Newcomers to the space industry are emphasizing the construction of the LEO satellite because of its cost. availability of non-shelf satellite components, as well as low launch costs due to the low satellite launch weight. The use of LEO satellites or satellites for satellite tracking applications, military surveillance and communications, and satellite-based internet services presents significant benefits due to its proximity to Earth. Its satellite-based installation is equally beneficial for delivering important data and environment for monitoring and resources. Also, these satellites are used for the satellite deorbiting process. This development is expected to drive the market forward.
"Growing Satellite Consumer Applications to Promote Market Growth Due to High Satellite Delivery and Explosion Demand"
The high demand for satellite thinking software, launch programs, and the need for promotional programs is expected to further market growth during forecasting. Rising national security threats and national security concerns have prompted governments around the world to use satellite imagery systems. Industries, defense organizations, and governments are planting satellite-based images for a variety of applications such as natural resource mapping, weather forecasting, and important data for military and national security applications. Satellite thinking can also be used to track geospatial data, powerful human interventions such as urban outcomes, satellite imagery for various oil and gas satellites, mining, and spatial information systems. Satellite imagery also focuses on applications such as engineering and construction, disaster response, conservation, and research, as well as media and entertainment.
RESTRAINTS
In recent decades, there have been several spatial launches in many countries around the world. The introduction of the atmosphere is one of the reasons for the production of high carbon emissions, due to the burning of solid rocket fuel. The launch of the atmosphere produces clouds of debris, which can change the atmosphere in a dangerous way. The pollutants and chemicals emitted by the alumina during the launch of the atmosphere deplete the ozone layer, resulting in the release of harmful gases. According to a United Nations Development Program report, Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) is being used in space programs as a rocket propellant responsible for transforming the Kazakh Steppe natural disaster area.
UDMH, which causes cancer in humans and rocket-propelled grenades during the first and second stages of the Russian proton, has damaged the environment. Proton has been a mainstay of various commercial and government satellites since 1965. Scientists and environmentalists have observed the UDMH deposit on the ground and its products for decades. The report also states that solid rocket motors are responsible for launching heavy-duty vehicles and burning a mixture of ammonia and aluminum. For example, NASA's solid rockets also fired the same mixture, producing large clouds of active chemicals such as aluminum oxide and hydrochloric acid during the space launch. These clouds disrupt soil and water quality and disrupt and stop plant growth.
OPPORTUNITIES
The market for space propulsion has been steadily expanding in recent years. Due to a growth in commercial applications throughout the world, this industry is expected to grow rapidly in the next years. To address the broad and expanding demand from non-military purposes, manufacturers are doing extensive research and development in advanced space propulsion technologies like nuclear propulsion, antimatter propulsion, and electric sail propulsion. The focus of R&D is on creating creative and efficient propulsion systems and technologies, with equal attention to quality and safety, among other considerations. Major corporations are investing heavily in their own R&D departments and developing operational prototypes in order to secure high-value, long-term contracts in the space propulsion industry, which is expected to grow at an exponential rate.
CHALLENGES
The phrase "space debris" refers to the inadvertent and unmanaged fall onto Earth of no longer functioning space spacecraft or parts of any size. Since the dawn of human space exploration, the number of variously characterized objects in orbit around the Earth has quickly increased, and the trend is continuing now more than ever with the current generation of small satellites. According to NASA and the European Space Agency's web pages, there are around 150 million objects with a total mass of more than 5,000 tonnes floating between lower Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) at a distance of up to 10,000 kilometers from Earth's surface. Because tiny satellites are often launched, they may pose a threat.
The phrase "space debris" refers to the inadvertent and unmanaged fall onto Earth of no longer functioning space spacecraft or parts of any size. Since the dawn of human space exploration, the number of variously characterized objects in orbit around the Earth has quickly increased, and the trend is continuing now more than ever with the current generation of small satellites. According to NASA and the European Space Agency's web pages, there are around 150 million objects with a total mass of more than 5,000 tonnes floating between lower Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) at a distance of up to 10,000 kilometers from Earth's surface. Because tiny satellites are often launched, they may pose a threat.
THE IMPACT OF COVID-19
Many launch service providers are concentrating on prospective launches that have been postponed. For the time being, Rocket Lab has halted launches. Flights at the Guiana Space Center, a French and European spaceport, have been halted. The French company Arianespace continues to launch from Baikonur, Russia. In April 2020, a new crew for the International Space Station (ISS) was launched by Soyuz MS-16, and on August 18, 2020, SpaceX launched its 11th Starlink mission, which comprised 58 Starlink satellites and three of Planet's SkySats.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has had an influence on the space sector, which had moderate to lower growth in 2020 and is expected to continue to expand during the projected period. affected by a manufacturing standstill or constrained manufacturing capability owing to the adoption of Jockdown across the board, Due to the divergence of the budget to combat the spread of the pandemic and related infrastructure expenditures, the budget of governmental or commercial market players for the space industry development or space launches has decreased.
KEY MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Platform
-
Satellites
-
Cubesats
-
Small Satellites
-
Microsatellites
-
Minisatellites
-
Medium Satellites (500-2,500 Kg)
-
Large Satellites (>2,500kg)
-
-
Capsules\Cargos
-
Crewed Spacecraft Or Human Space Flight
-
Uncrewed Or Unmanned Spacecraft
-
-
Interplanetary Spacecraft & Probes
-
Rovers/Spacecraft Landers
-
Launch Vehicles
-
Small Launch Vehicles (<350,000 Kg)
-
Medium To Heavy Launch Vehicles (>350,000 Kg)
-
Reusable Launch Vehicles
-
By Propulsion Type
-
Chemical Propulsion
-
Solid
-
Homogeneous
-
Composites/ Heterogeneous
-
-
Liquid
-
Monopropellant
-
Non-Green
-
Green
-
-
Bi-Propellent
-
Hypergolic
-
-
Hybrid
-
Cold Gas
-
-
Non-Chemical Propulsion
-
Electric Or Ion Propulsion
-
Electrothermal
-
Argon
-
Hydrogen
-
Others
-
-
Electromagnetic
-
Ptfe
-
-
Electrostatic
-
Xenon
-
Krypton
-
-
-
Solar Propulsion
-
Solar Sail Propulsion
-
Solar Electric Propulsion (Sep)
-
Solar Thermal Propulsion
-
-
-
Tether Propulsion
-
Nuclear Propulsion
-
Laser Propulsion
By System Component
-
Thrusters
-
Chemical Thrusters
-
Cold & Warm Gas Thruster’s
-
Mono propellant Thruster’s
-
Bipropellant Thrusters
-
-
Electric Or Ion Thruster
-
Gridded Electrostatic Ion Thrusters
-
Hall Effect Thrusters
- Field-Emission Electric Propulsion
- Pulsed Plasma Thruster (Ppt)
- Magneto Plasma Dynamic (Mpd) Thruster
-
-
-
Propellant Feed Systems
-
Propellant Tanks
-
Monopropellant Tanks
-
Bipropellant Tanks
-
Oxidiser Tank
-
-
Flow And Pressure Regulators
-
Valves
-
Turbopumps
-
Combustion Chambers
-
-
Rocket Motors
-
Nozzles
-
Propulsion Thermal Control
-
Power Processing Units
-
Others
By Orbit
-
Low Earth Orbit (Leo)
-
Medium Earth Orbit (Meo)
-
Geostationary Earth Orbit (Geo)
-
Beyond Geosynchronous Orbit
By End Use
-
Commercial
-
Satellite Operators And Owners
-
Space Launch Service Providers
-
Government & Defense
-
Departments Of Defense
-
National Space Agencies
-
Others
By Support Systems
-
Design, Engineering, Operation & Maintenance
-
Hot Firing & Environmental Test Execution
-
Fueling & Launch And Ground Support
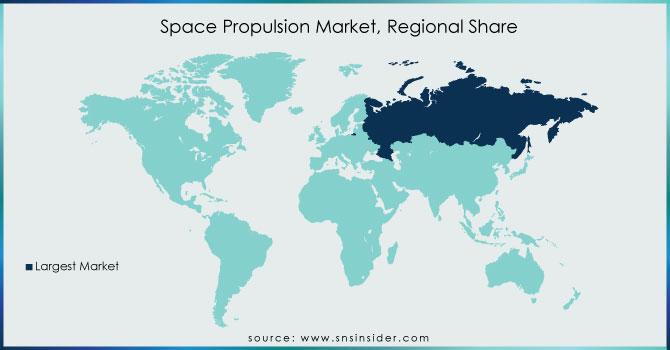
Regional Analysis
Several governments throughout the world have launched satellites into space over the years. Due to the burning of solid rocket fuels, space launches are one of the major sources of carbon emissions. Exhaust clouds from space launches can cause harmful changes in the environment. Because of the production of harmful gases, the pollution and chemicals produced by alumina during space launches destroy the ozone layer. Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) is used in space systems as rocket fuel, according to a UNDP assessment, and is responsible for changing the Kazakh Steppe into an ecological catastrophe zone. spending on infrastructure The UDMH, which is highly carcinogenic to humans and spills from the first and second stage rockets of Russia's Proton launch vehicle, has harmed the environment. Since 1965, Proton has been the primary launch vehicle for a variety of commercial and government satellites. For decades, scientists and environmentalists have been seeing the UDMH deposit in the soil and its consequences. Solid rocket engines are also responsible for launching large lift launch vehicles and combusting a combination of ammonia and aluminum, according to the paper. During space launches, NASA's solid rocket boosters, for example, burn the same mix, resulting in huge clouds of reactive chemicals like aluminum oxide and hydrochloric acid. These clouds have an impact on soil and water quality, as well as disrupting and stunting plant development.
Need any customization research on Space Propulsion Market - Enquiry Now
REGIONAL COVERAGE:
North America
-
USA
-
Canada
-
Mexico
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
The Netherlands
-
Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
China
-
India
-
Australia
-
Rest of Asia-Pacific
The Middle East & Africa
-
Israel
-
UAE
-
South Africa
-
Rest of Middle East & Africa
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
Rest of Latin America
Key Players
The Major Players are IHI Corporation, Moog Inc., Blue Origin, Northrop Grumman Corporation.,Space Exploration Technologies Corp, Accion Systems Inc., Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings Inc., Honeywell International Inc., Sierra Nevada Corporation,Safran SA & Other Players
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 9.76 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | US$ 27.8 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 11.37 % From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments |
|
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (USA, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (Japan, South Korea, China, India, Australia, Rest of Asia-Pacific), The Middle East & Africa (Israel, UAE, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | IHI Corporation, Moog Inc., Blue Origin, Northrop Grumman Corporation.,Space Exploration Technologies Corp, Accion Systems Inc., Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings Inc., Honeywell International Inc., Sierra Nevada Corporation,Safran SA. |

