
Get more information on Mexico GCC Market - Request Free Sample Report
The Mexico GCC Market Size was valued at USD 5.29 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 18.60 Billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 13.42% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Mexico’s emergence as a leading hub for Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in Latin America has been bolstered by a combination of strategic location, competitive labor costs, and a highly skilled workforce. The country's economic stability, combined with its proximity to the United States and integration into global trade frameworks such as the USMCA, has driven a surge in foreign investment.
According to recent estimates, the total number of GCCs in Mexico has increased by 17% annually over the past five years. As of 2024, over 150 multinational corporations (MNCs) operate GCCs in Mexico, employing more than 180,000 people. The growth trajectory remains strong, with projections suggesting the GCC workforce could exceed 250,000 by 2030.
Proximity to the U.S. and Cost Advantages
Mexico’s proximity to the United States is one of its most significant competitive advantages in the GCC market. Companies benefit from operational cost reductions of up to 50%, compared to maintaining similar operations in the U.S. For example, while the average cost of operating a back-office GCC in the U.S. can range from USD 90,000 to USD 120,000 annually per employee, similar positions in Mexico can be filled at a cost of USD 40,000 to USD 60,000 per year.
Time zone alignment allows for real-time collaboration between U.S.-based headquarters and Mexican GCCs, leading to a reduction in project delays and an increase in efficiency. Over 65% of U.S.-based companies with nearshore operations in Mexico report faster project completion times and reduced overhead costs.
Skilled Workforce and Talent Pool
The availability of a highly skilled workforce is a key driver of GCC growth in Mexico. Over 110,000 engineers graduate from Mexican universities annually, and this number is expected to increase by 5% year-on-year over the next decade. This makes Mexico the largest supplier of engineering talent in Latin America, surpassing Brazil and Argentina combined.
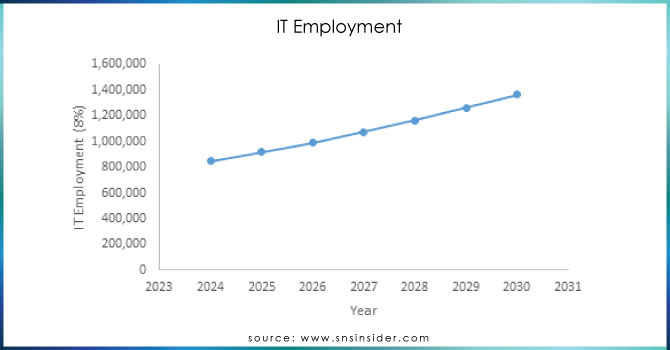
The country's total IT workforce now exceeds 850,000, with 280,000 of these professionals involved in advanced sectors such as software development, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. Mexico’s technology talent is increasingly recognized as one of the most cost-effective in the region, with the average salary for IT specialists ranging from USD30,000 to USD45,000, considerably lower than their counterparts in the U.S.
Government Policies Supporting GCCs
Mexico's government has implemented several policies to encourage the growth of GCCs. For instance, through the "Maquiladora Program" (IMMEX), companies setting up nearshore operations in Mexico benefit from tax incentives, allowing them to import materials and equipment duty-free, as long as the products are eventually exported. As a result, the program has contributed to a 22% increase in the number of manufacturing-related GCCs in Mexico since 2018.
In addition, the government’s collaboration with private sector firms has led to the development of 37 technology parks and innovation centers across the country, providing advanced infrastructure, high-speed internet, and data security. These parks house over 120,000 employees and are expected to generate an additional USD4 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI) by 2025.
Emerging Nearshore Services
Mexico’s nearshore service offerings have expanded rapidly in recent years, with sectors such as IT, finance, and customer support experiencing growth rates of 12% to 15% annually. As of 2024, nearly 80% of Mexico’s GCC workforce is employed in nearshore operations for U.S. and Canadian companies.
This shift toward nearshore services has also led to an increase in the complexity of services provided by GCCs in Mexico. Over 60% of GCCs now offer advanced services, including R&D, data analytics, and software development, compared to just 35% in 2015. This transition has helped position Mexico as a global leader in nearshore outsourcing, particularly in the IT and technology sectors.
1- Key Trends in the GCC Landscape
Evolution of Mexico as a Hub for Centers of Excellence (CoEs)
Mexico’s reputation as a Center of Excellence (CoE) hub is solidifying, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and financial services. The country currently hosts more than 50 CoEs, an increase of 40% from five years ago. These centers focus on advanced technological innovation, product development, and process optimization, supporting global operations for companies like General Motors, Honeywell, and Continental.
The automotive CoEs in Mexico, for example, now contribute to nearly 20% of the total R&D output of multinational automotive firms, developing solutions for electric vehicles, autonomous driving technologies, and emissions control. In the IT sector, over 25% of all GCCs now have dedicated CoEs for software development and digital transformation.
Multinational Investments
Mexico is ranked 9th worldwide for attracting foreign investments, with Mexico City accounting for 32% of this investment during the first three quarters of 2023. The USMCA agreement with the United States and Canada enhances Mexico's appeal as a preferred destination in Latin America, especially for sectors such as Automotive, Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, and Medical Devices. In 2022, Mexico established the 'Invest in Mexico' business center to facilitate and support foreign investors in establishing their operations within the country.
Mexico's attractiveness to multinationals has resulted in substantial investments from global giants. For example, IBM has invested over USD 500 million in expanding its operations in Guadalajara, while Microsoft’s planned investment in Mexico will exceed USD1.1 billion by 2025. These investments are part of broader efforts to develop CoEs in emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity.
As of 2024, more than 60% of the world's largest companies have established at least one GCC in Mexico, and FDI in Mexico’s GCC sector reached USD 3.2 billion in 2023, a 12% increase from the previous year.
Investment in the IT sector has grown the fastest, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14% over the past five years. The manufacturing sector follows closely, with a CAGR of 12%. The financial services sector has seen slower but steady growth, averaging 8% annually.
2- Factors Driving the Growth of GCCs in Mexico
Infrastructure Development
Mexico’s infrastructure improvements have played a crucial role in supporting the growth of GCCs. The country has invested over USD 30 billion in infrastructure projects over the past decade, including the development of high-speed internet networks and the modernization of airports, highways, and ports. Guadalajara, Monterrey, and Mexico City have become key hubs for tech infrastructure, housing the majority of Mexico's IT and CoE centers.
By 2025, Mexico is expected to have 95% internet penetration in urban areas, further enabling the growth of tech-based GCCs. The country's data center capacity has also expanded, with over 1.5 million square feet of new data center space expected to come online by 2026.
Economic Stability and Trade Policies
Mexico’s economic stability, despite occasional political fluctuations, has provided a solid foundation for long-term investment. The country’s inflation rate has remained below 5% in recent years, and its GDP growth is expected to remain steady at around 3% annually over the next five years. This stability, combined with Mexico’s integration into major trade agreements like the USMCA and the Trans-Pacific Partnership, has created a conducive environment for multinational corporations to set up GCCs.
Furthermore, Mexico has signed over 30 free trade agreements with more than 50 countries, ensuring that products and services developed in Mexican GCCs can be exported duty-free to some of the world’s largest markets.
Rising Skill Set and Engineer Availability
The rising skill set of Mexico’s workforce is a crucial factor driving the growth of GCCs. Over the past decade, Mexico has consistently ranked among the top three countries in Latin America in terms of workforce competitiveness. In addition to the 110,000 annual engineering graduates, more than 200,000 students are enrolled in STEM programs, preparing to enter the job market by 2030.
Moreover, specialized training programs funded by both the Mexican government and private sector firms have contributed to the growth of a workforce skilled in advanced technologies, such as robotics, AI, and blockchain. These programs ensure that Mexico’s GCCs remain competitive in high-tech industries that require a continuous supply of talent.
3- Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
Mexico’s primary challenge remains political uncertainty. Changes in political leadership could result in shifts in economic policies that affect the business climate, particularly with regard to trade agreements and foreign investment incentives. Additionally, the country faces rising competition from other emerging markets in Asia and Eastern Europe, which offer even lower labor costs for certain types of GCC operations.
Mexico must also address regional disparities in infrastructure development. While cities like Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Monterrey are well equipped to handle the needs of multinational corporations, many rural areas still lack the necessary telecommunications and transportation infrastructure to support large-scale GCCs.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, Mexico presents numerous opportunities for growth in the GCC market. The country's focus on Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation and AI, is expected to drive the next wave of GCC investment. By 2030, more than 70% of all new GCCs in Mexico are expected to involve some form of advanced digital transformation.
Additionally, Mexico’s burgeoning fintech sector, combined with its leadership in manufacturing, presents a unique opportunity for companies to develop integrated supply chain and financial services GCCs. These operations would allow companies to leverage Mexico’s expertise in both manufacturing and financial technology to optimize global operations.
By Industry
Sectors Leading the GCC Wave
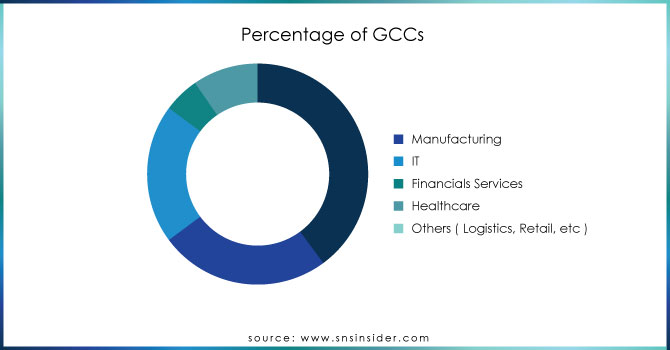
Manufacturing: Mexico’s manufacturing GCCs account for 40% of all GCC operations in the country. The automotive industry remains the largest contributor, with over 45,000 employees engaged in manufacturing-related GCC activities. Mexico now produces 4 million vehicles annually, making it the 7th largest automotive producer globally.
Technology: The IT sector is the fastest-growing segment within Mexico’s GCC landscape. In 2023 alone, over USD 2.5 billion was invested in setting up new IT-focused GCCs. Mexico now ranks as the top location in Latin America for IT outsourcing, with 180,000 employees dedicated to digital services across the country’s IT GCCs.
Financial Services: Mexico has also become a hub for financial services GCCs, with more than 20% of these centers focusing on banking, insurance, and fintech. The number of financial service providers operating GCCs in Mexico has grown by 25% annually since 2019, and this sector now employs over 50,000 professionals across various roles, including customer support, compliance, and back-office processing.
Mexico vs. Brazil
Mexico’s cost structure is approximately 15% lower than Brazil’s for most GCC operations, particularly in the technology and manufacturing sectors. In terms of infrastructure, Mexico has a more developed telecommunications network and greater political stability, making it a preferred choice for many multinationals.
While Brazil remains a strong player, particularly in sectors like energy and natural resources, Mexico’s proximity to the U.S. and its superior transportation infrastructure give it a decisive edge over Brazil for nearshore operations. Mexico’s overall FDI inflow is also consistently higher than Brazil’s, with Mexico attracting USD32 billion in 2023, compared to Brazil’s USD24 billion.
Mexico vs. Argentina
Argentina’s economic volatility, with inflation rates exceeding 80% in recent years, has created significant challenges for businesses operating in the country. In contrast, Mexico’s inflation rate has remained below 5%, and the country has consistently attracted more foreign direct investment due to its stable business environment.
Argentina's talent pool is strong in certain areas, particularly software development, but its high labor costs and economic instability have limited its ability to compete with Mexico. As a result, Mexico’s GCC sector is more robust, attracting significantly more.
Top Industries of Companies Investing in Mexico
Industrial:
Honeywell
Eaton
HITACHI
ABB
Rockwell Automation
Mexico’s position as a global hub for GCCs is firmly established, with strong growth expected across multiple sectors, including IT, manufacturing, and financial services. The country’s competitive labor costs, proximity to the U.S., and skilled workforce have driven substantial foreign investment, and these trends are expected to continue in the years ahead.
By addressing infrastructure disparities and leveraging opportunities in advanced digital technologies, Mexico can further solidify its position as a premier destination for multinational corporations seeking nearshore solutions. The data and statistics presented in this report demonstrate Mexico’s capacity to continue leading the GCC market in Latin America and beyond.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 5.29 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | US$ 18.60 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 13.42 % From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | By Industry (Manufacturing, IT, Financial Services, Healthcare, Others) |
| Company Profiles | Faurecia, Suzuki, VOLVO, Continental, Nestle, PEPSICO, ADM, AB InBev, SIEMENS, Honeywell, Eaton, HITACHI, ABB, Rockwell Automation |
| Key Drivers | • Mexico’s infrastructure improvements have played a crucial role in supporting the growth of GCCs • Mexico’s economic stability, despite occasional political fluctuations, has provided a solid foundation for long-term investment. |
| Restraints | • Mexico’s primary challenge remains political uncertainty |
The Mexico GCC Market was valued at USD 5.29 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 18.60 Billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 13.42% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Answer: Mexico is considered a top destination for GCCs due to several factors, including its proximity to the United States, a skilled workforce, competitive labor costs, and a stable business environment. The country has a strong talent pipeline, producing over 110,000 engineering graduates annually, and is well-equipped to support various industries, including IT, manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals.
Answer: The sectors driving investment in Mexico's GCC market include Automotive, Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Medical Devices, and IT services. The USMCA agreement has further enhanced Mexico's attractiveness for these industries by providing favorable trade terms and incentives for foreign investments.
Answer: Mexico faces several challenges in attracting GCC investments, including political uncertainty, potential changes in trade policies, and competition from emerging markets with lower labor costs. Additionally, regional disparities in infrastructure development may hinder the growth of GCCs in less developed areas.
Answer: Mexico is addressing its challenges by promoting advanced technologies, such as automation and AI, to enhance its GCC offerings. The government has launched initiatives like the 'Invest in Mexico' business center to attract foreign investors and facilitate business setup. By improving infrastructure and fostering innovation, Mexico aims to solidify its position as a leading destination for GCCs in Latin America.
Table of Content
1. Introduction
1.1 Market Definition
1.2 Scope (Inclusion and Exclusions)
1.3 Research Assumptions
2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Overview
2.2 Regional Synopsis
2.3 Competitive Summary
3. Research Methodology
3.1 Top-Down Approach
3.2 Bottom-up Approach
3.3. Data Validation
3.4 Primary Interviews
4. Market Dynamics Impact Analysis
4.1 Market Driving Factors Analysis
4.1.1 Drivers
4.1.2 Restraints
4.1.3 Opportunities
4.1.4 Challenges
4.2 PESTLE Analysis
4.3 Porter’s Five Forces Model
5. Statistical Insights and Trends Reporting
5.1 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Trends, By Industry (2023)
5.2 Workforce and Talent Pool
5.3 Industry-Specific Data for GCC
5.4 Infrastructure and Business Environment
6. Competitive Landscape
6.1 List of Major Companies, By Region
6.2 Market Share Analysis, By Region
6.3 Product Benchmarking
6.3.1 Product specifications and features
6.3.2 Pricing
6.4 Strategic Initiatives
6.4.1 Marketing and promotional activities
6.4.2 Distribution and supply chain strategies
6.4.3 Expansion plans and new product launches
6.4.4 Strategic partnerships and collaborations
6.5 Technological Advancements
6.6 Market Positioning and Branding
7. Mexico GCC Market Segmentation, By Industry
7.1 Chapter Overview
7.2 Manufacturing
7.2.1 Manufacturing Market Trends Analysis (2020-2032)
7.2.2 Manufacturing Market Size Estimates and Forecasts to 2032 (USD Billion)
7.3 IT
7.3.1 IT Market Trends Analysis (2020-2032)
7.3.2 IT Market Size Estimates and Forecasts to 2032 (USD Billion)
7.4 Financial Services
7.4.1 Financial Services Market Trends Analysis (2020-2032)
7.4.2 Financial Services Market Size Estimates and Forecasts to 2032 (USD Billion)
7.5 Healthcare
7.5.1 Healthcare Market Trends Analysis (2020-2032)
7.5.2 Healthcare Market Size Estimates and Forecasts to 2032 (USD Billion)
7.6 Others
7.6.1 Others Market Trends Analysis (2020-2032)
7.6.2 Others Market Size Estimates and Forecasts to 2032 (USD Billion)
8. Company Profiles
8.1 Faurecia
8.1.1 Company Overview
8.1.2 Financial
8.1.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.1.4 SWOT Analysis
8.2 Suzuki
8.2.1 Company Overview
8.2.2 Financial
8.2.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.2.4 SWOT Analysis
8.3 VOLVO
8.3.1 Company Overview
8.3.2 Financial
8.3.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.3.4 SWOT Analysis
8.4 Continental
8.4.1 Company Overview
8.4.2 Financial
8.4.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.4.4 SWOT Analysis
8.5 Nestle
8.5.1 Company Overview
8.5.2 Financial
8.5.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.5.4 SWOT Analysis
8.6 PEPSICO
8.6.1 Company Overview
8.6.2 Financial
8.6.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.6.4 SWOT Analysis
8.7 ADM
8.7.1 Company Overview
8.7.2 Financial
8.7.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.7.4 SWOT Analysis
8.8 AB InBev
8.8.1 Company Overview
8.8.2 Financial
8.8.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.8.4 SWOT Analysis
8.9 SIEMENS
8.9.1 Company Overview
8.9.2 Financial
8.9.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.9.4 SWOT Analysis
8.10 Honeywell
8.10.1 Company Overview
8.10.2 Financial
8.10.3 Products/ Services Offered
8.10.4 SWOT Analysis
9. Use Cases and Best Practices
10. Conclusion
An accurate research report requires proper strategizing as well as implementation. There are multiple factors involved in the completion of good and accurate research report and selecting the best methodology to compete the research is the toughest part. Since the research reports we provide play a crucial role in any company’s decision-making process, therefore we at SNS Insider always believe that we should choose the best method which gives us results closer to reality. This allows us to reach at a stage wherein we can provide our clients best and accurate investment to output ratio.
Each report that we prepare takes a timeframe of 350-400 business hours for production. Starting from the selection of titles through a couple of in-depth brain storming session to the final QC process before uploading our titles on our website we dedicate around 350 working hours. The titles are selected based on their current market cap and the foreseen CAGR and growth.
The 5 steps process:
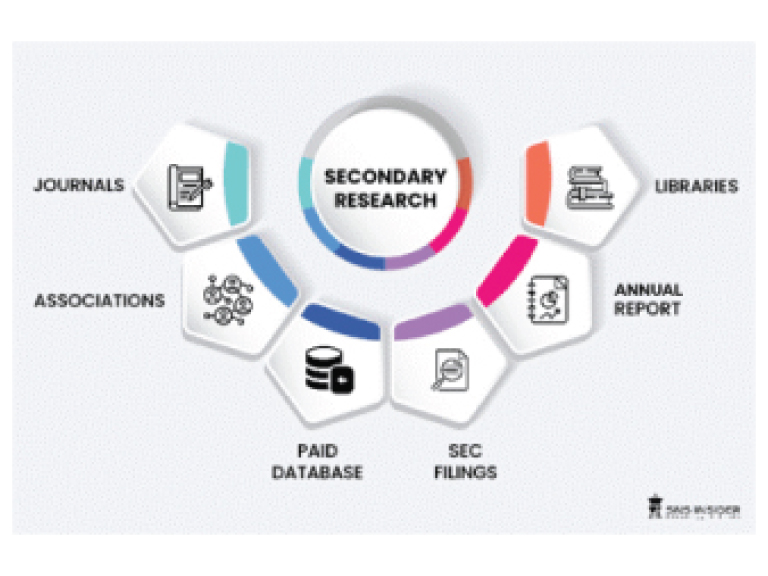
Step 1: Secondary Research:
Secondary Research or Desk Research is as the name suggests is a research process wherein, we collect data through the readily available information. In this process we use various paid and unpaid databases which our team has access to and gather data through the same. This includes examining of listed companies’ annual reports, Journals, SEC filling etc. Apart from this our team has access to various associations across the globe across different industries. Lastly, we have exchange relationships with various university as well as individual libraries.
Step 2: Primary Research
When we talk about primary research, it is a type of study in which the researchers collect relevant data samples directly, rather than relying on previously collected data. This type of research is focused on gaining content specific facts that can be sued to solve specific problems. Since the collected data is fresh and first hand therefore it makes the study more accurate and genuine.
We at SNS Insider have divided Primary Research into 2 parts.
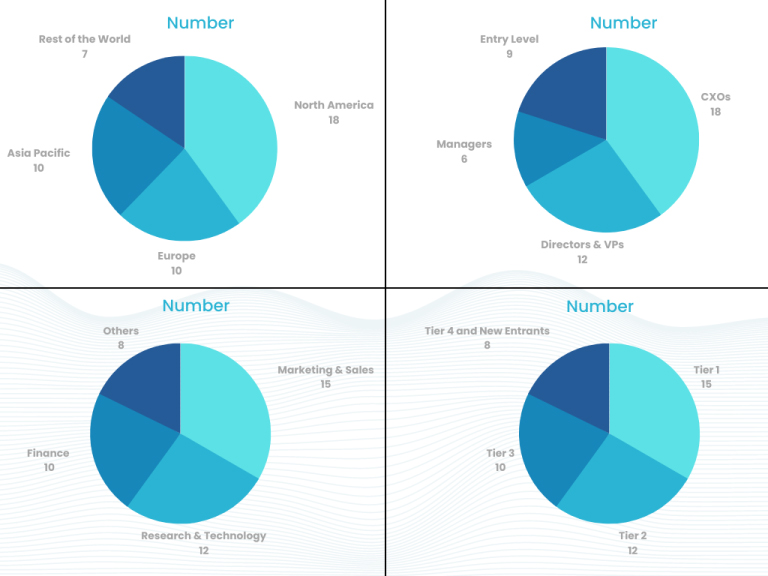
Part 1 wherein we interview the KOLs of major players as well as the upcoming ones across various geographic regions. This allows us to have their view over the market scenario and acts as an important tool to come closer to the accurate market numbers. As many as 45 paid and unpaid primary interviews are taken from both the demand and supply side of the industry to make sure we land at an accurate judgement and analysis of the market.
This step involves the triangulation of data wherein our team analyses the interview transcripts, online survey responses and observation of on filed participants. The below mentioned chart should give a better understanding of the part 1 of the primary interview.
Part 2: In this part of primary research the data collected via secondary research and the part 1 of the primary research is validated with the interviews from individual consultants and subject matter experts.
Consultants are those set of people who have at least 12 years of experience and expertise within the industry whereas Subject Matter Experts are those with at least 15 years of experience behind their back within the same space. The data with the help of two main processes i.e., FGDs (Focused Group Discussions) and IDs (Individual Discussions). This gives us a 3rd party nonbiased primary view of the market scenario making it a more dependable one while collation of the data pointers.
Step 3: Data Bank Validation
Once all the information is collected via primary and secondary sources, we run that information for data validation. At our intelligence centre our research heads track a lot of information related to the market which includes the quarterly reports, the daily stock prices, and other relevant information. Our data bank server gets updated every fortnight and that is how the information which we collected using our primary and secondary information is revalidated in real time.

Step 4: QA/QC Process
After all the data collection and validation our team does a final level of quality check and quality assurance to get rid of any unwanted or undesired mistakes. This might include but not limited to getting rid of the any typos, duplication of numbers or missing of any important information. The people involved in this process include technical content writers, research heads and graphics people. Once this process is completed the title gets uploader on our platform for our clients to read it.
Step 5: Final QC/QA Process:
This is the last process and comes when the client has ordered the study. In this process a final QA/QC is done before the study is emailed to the client. Since we believe in giving our clients a good experience of our research studies, therefore, to make sure that we do not lack at our end in any way humanly possible we do a final round of quality check and then dispatch the study to the client.
By Industry
Manufacturing
IT
Financial Services
Healthcare
Others
Request for Segment Customization as per your Business Requirement: Segment Customization Request
Available Customization
With the given market data, SNS Insider offers customization as per the company’s specific needs. The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
Criss-Cross segment analysis (e.g. Product X Application)
Product Matrix which gives a detailed comparison of product portfolio of each company
Geographic Analysis
Additional countries in any of the regions
Company Information
Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (Up to five)
The Online Gambling & Betting Market was valued at USD 81.86 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 218.02 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11.54% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The Passenger Information System Market Size was USD 29.5 Billion in 2023 and will reach USD 90.8 Billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 12.12% by 2024-2032.
IT Asset Management (ITAM) Software Market Size was valued at USD 1.7 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 2.9 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.2% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Geospatial Imagery Analytics Market size was valued at USD 15.8 Billion in 2023 and will grow to USD 197.4 Billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 32.4% by 2032.
The Project Portfolio Management Market Size was valued at USD 4.75 Billion in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 8.82 Billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 7.44%.
Threat Modeling Tools Market was valued at USD 0.95 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 3.37 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.17% from 2024-2032.
Hi! Click one of our member below to chat on Phone